Workflow Tool»
The Workflow Tool stack setting allows you to choose between three options:
- OpenTofu.
- Terraform (FOSS).
- Custom.
The OpenTofu and Terraform (FOSS) options give you out of the box support for using OpenTofu and for open source versions of Terraform respectively. When you use either of those options, all you need to do is choose the version you want to use and you're good to go.
The rest of this page explains the Custom option. This option allows you to customize the commands that are executed as part of Spacelift's Terraform workflow. This can be useful if you want to run a custom binary instead of one of the OpenTofu or Terraform versions supported out the box by Spacelift.
Info
Note that any custom binary is considered third-party software and you need to make sure you have the necessary rights (e.g. license) to use it.
How does it work?»
Each stage of the Terraform workflow uses certain commands to perform tasks such as generating a Terraform plan, or getting the current state. We provide a built-in set of commands to use for Terraform, but you can also specify your own custom commands. You do this via a file called .spacelift/workflow.yml.
The following is an example of what the workflow commands look like for Terraform:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | |
How to configure a custom tool»
To use a custom tool, three things are required:
- A way of providing the tool to your runs.
- A way of specifying the commands that should be executed.
- Indicating that you want to use a custom tool on your stack/module.
Providing a tool»
There are two main ways of providing a custom tool:
- Using a custom runner image.
- Using a before_init hook to download your custom tool.
Specifying the commands»
Your custom workflow commands need to be provided in a workflow.yml file stored in the .spacelift folder at the root of your workspace. There are three main ways of providing this:
- Via a mounted file in the stack's environment.
- Via a mounted file stored in a context
- Directly via your Git repo.
The option you choose will depend on your exact use-case, for example using the stack's environment allows you to quickly test out a new custom tool, using a context allows you to easily share the same configuration across multiple stacks, and storing the configuration in your Git repo allows you to track your settings along with the rest of your code.
Here is an example configuration to use a fictional tool called super-iac:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
Using a custom tool on a Stack/Module»
To update your Stack/Module to use a custom workflow tool, edit the Workflow tool setting in the Vendor settings:
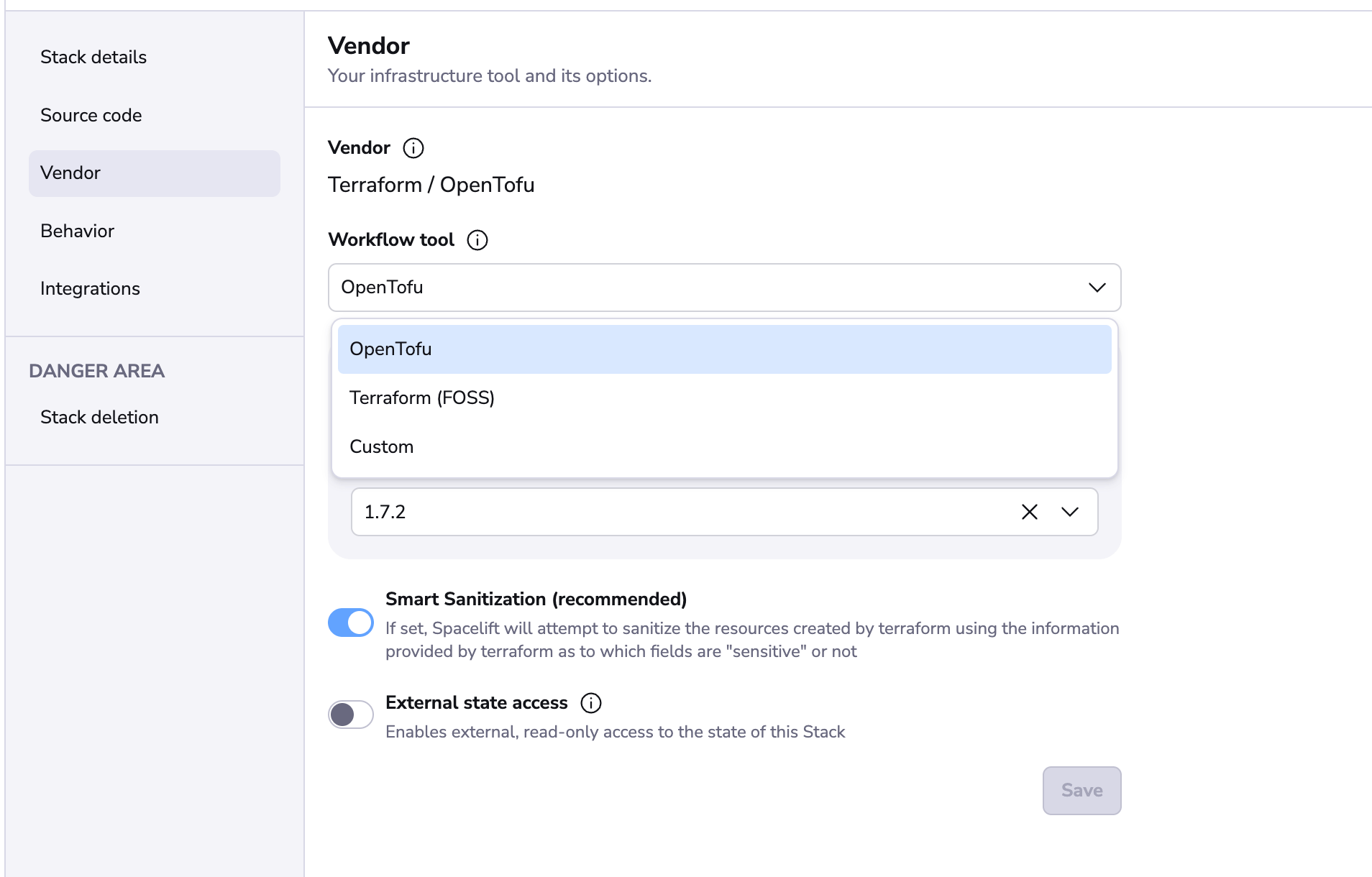
When you choose the Custom option, the version selector will disappear:
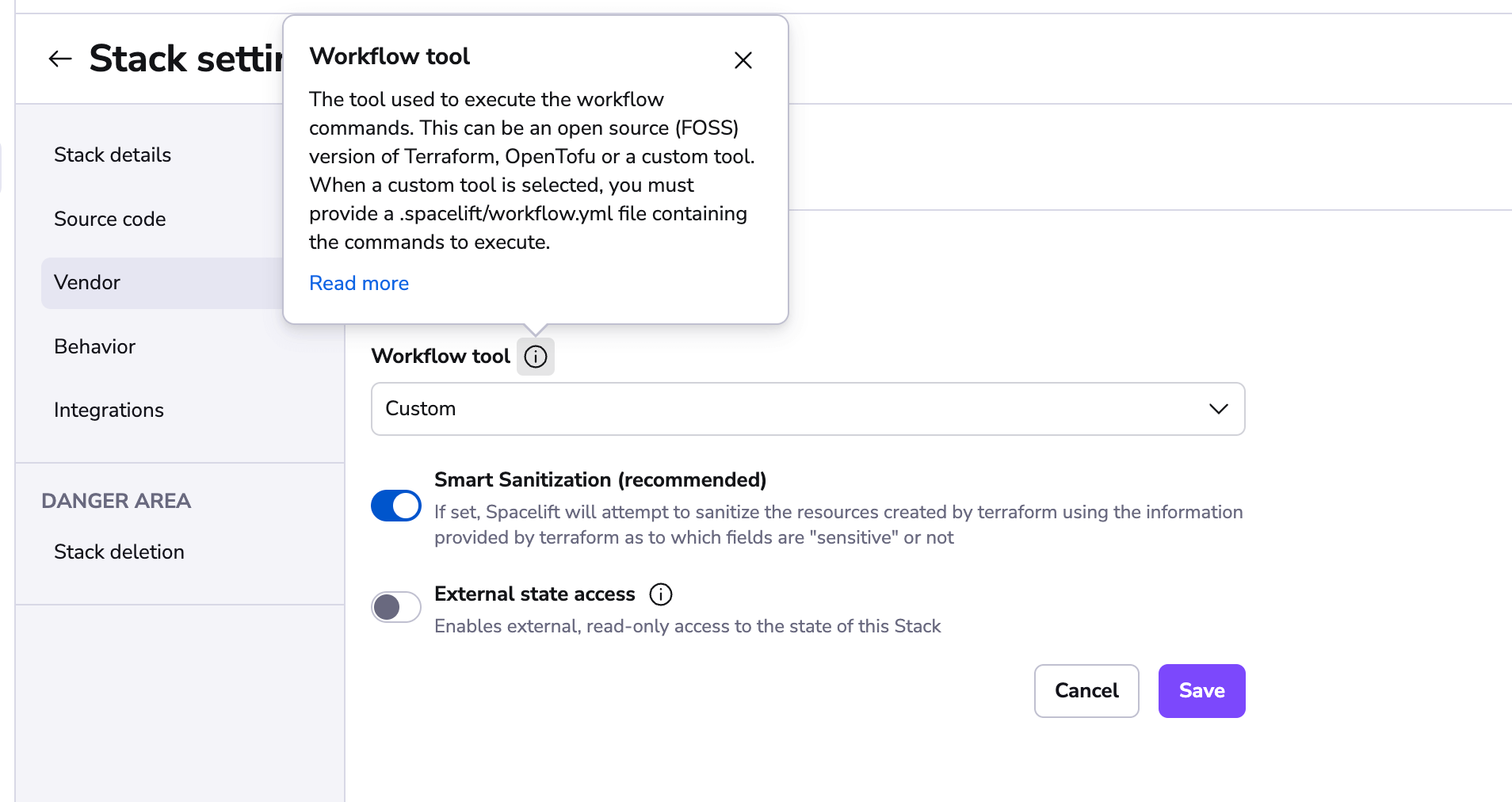
This is because you are responsible for ensuring that the tool is available to the Run, and Spacelift will not automatically download the tool for you.
Runtime Configuration»
You can also use runtime configuration to configure the workflow tool for a stack or module. This allows you to try out a different configuration as part of a PR without adjusting your stack/module settings.
The following example shows how to configure a particular stack to use a custom tool:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
The following example shows how to do the same for a module test case:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Troubleshooting»
Workflow file not found»
If no workflow.yml file has been created but your Stack has been configured to use a custom tool, you may get an error message like the following:
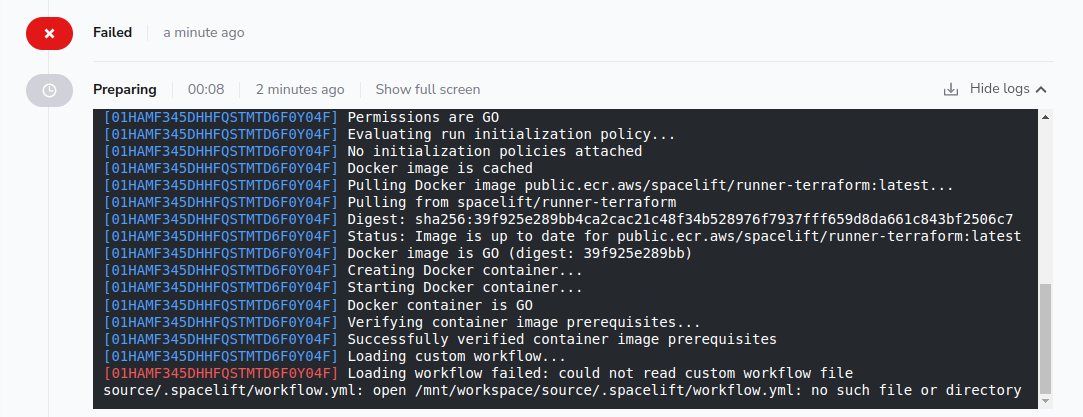
If this happens, please ensure you have added a .spacelift/workflow.yml file to your Git repository, or attached it to your Stack's environment via a mounted file.
Commands missing»
If your .spacelift/workflow.yml does not contain all the required command definitions, or if any commands are empty, you will get an error message like the following:
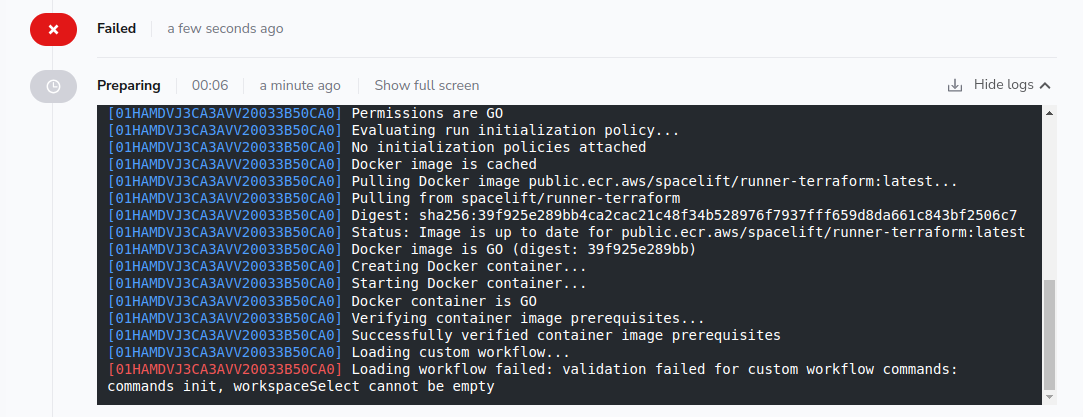
This check is designed as a protection mechanism in case new commands are added but your workflow hasn't been updated. In this case, please provide an implementation for the specified commands (in the example the init and workspaceSelect commands),
Tool not found»
If your custom tool binary cannot be found you will get an error message like the following:
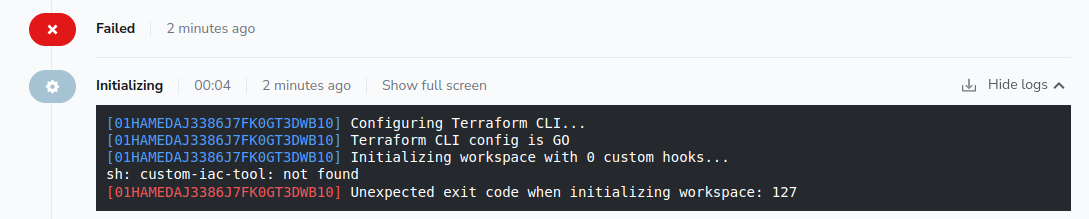
In this situation, please ensure that you are providing a custom workflow tool via a custom runner image or workflow hook.